1st year Chemistry Chapter 6 important notes:
1. In_____ the electron pairs in the central atom are
directed at 109o angle.
(a) H2O (b)
CO2 (c) CCl4 (d)
SO2
2. According
to electron pair repulsion theory shape of the molecule depends on____.
3. Which
of the following statements incorrect?
(A) The
anti-bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than the atomic orbital
(B) The
anti-bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than the bonding molecular
orbital
(C) The
anti-bonding molecular is equal in energy to the atomic orbital
(D) The
anti-bonding molecular orbital is higher in energy than the bonding molecular
orbital
(a) One
sigma and two Pi bonds (b) Two sigma and two Pi
bonds
(c) Only sigma
bonds (d)
Only Pi bonds
5. Nitrogen
molecule has____.
(a) One
Pi bond (b) Two Pi bonds (c) Two sigma bonds (d)
Three sigma bonds
6. The
correct order of decreasing bond energies in hydrogen halides is____.
(a) HCl
> HBr HCl > HF (b) Hl > HBr > HCl > HF (c) HI > HF > HCl > HBr (d)
HF > HCl > HBr > HF
7. Which
of the following has largest bond angle____.
(a) H2O (b) C2H4 (c) C2H6 (d)
C2H2
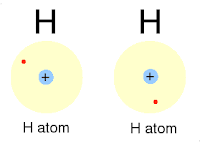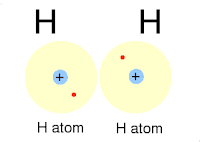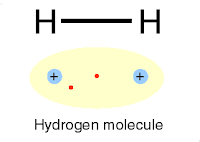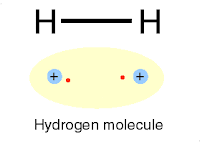 |
| Chemical bonding |
(a) Ionic
bond (b) Covalent bond (c) Dative bond (d) Polar bond
9. SP3
hybridization with one non-bonding electrons gives _____ structure.
(a) Bent
(b) Pyramidal (c) Tetrahedral (d) None of above
10. The
SI unit of dipole moment is____.
(a) Dynes (b)
Poise (c)
Coulomb meter (d) erg
11. The
covalent bonds are ____.
(a) Non
directional (b) Directional (c) Both A and B (d) None of above
12. Polar
compounds have relatively _____ melting and boiling point.
(a) Very
low (b)
low (c) Medium (d)
High
13. Polar
covalent bond is _____ than a non-polar covalent bond.
(a) Weaker (b)
Longer (c)
Stronger (d) None of above
14. The
angle between any two sp1 – hybridized orbitals is _____.
(a) 104 (b)
109 (c) 120 (d) 180
15. Ammonia
molecule has _____ electrons pair in its nitrogen atom.
(a) One (b)
Two (c) Three (d)
Four
16. BaO
is formed through_____.
(a) Ionic
bond (b) Covalent bond
(c) Dative bond (d) Metallic bond
17. Which
of the following is linear molecule?
(a) CO2
(b) H2O (c) SO2 (d) NH3
18. Which
of the following is the strongest bond?
(a) H-Cl
(b) H-F (c) H-I (d) H-Br
19. Ice
flouts on water due to____.
(a) Vander
Waal’s force (b) Low
freezing point (c) Low density (d) Minimum volume
20. Hydrogen
bonding is absent in___.
(a) H2O (b)
NH3 (c) C2H5OH
(d) C2H5OC2H5
21. The
hydrogen bond is also called____.
(a) Protonic
bridge (b) Primary bond (c) Tertiary bond (d) None of above
22. In
which compound carbon is sp3 hybridized____.
(a) HCOOH
(b) C2H2 (c)
C2H4 (d) CH3CHO
23. The
energy of antibonding molecular orbital is____.
(a) Greater
than the bonding M.O (b) Smaller than the bonding M.O
(c) Equal to that
of bonding M.O (d) None
of above
24. According
to VBT only____ orbitals take part in bond formation.
(a) Filled (b) Empty (c) Half filled (d)
Degenerate
25. Which
of the following is correct?
(a) Decreases
in bond length means increase in bond strength
(b) Radius
of carbon is less than that of nitrogen (c) Single bonds are stronger than double
bonds
(d) Bond energy is directly proportional to bond length
26. Which
of the following has least bond angle?
(a) BeF2 (b)
H2O (c) NH3 (d) CH4
27. How
many unpaired electrons are present in N+2 ?
(a) 1
(b) 2 (c) 3 (d)
4
28. The
example of the p-p orbital overlapping is the formation of___.
(a) H2
molecule (b) Cl2 molecule (c) Hydrogen chloride (d)
Hydrogen bromide
29. Fluorine
molecule is formed by the overlap of____.
(a) s-p
orbitals (b) s-s orbitals
(c) p-p orbitals by
head on overlapping (d)
p-p orbitals by side wise overlapping
30. In
co-ordinate bond, the acceptor atom must contains in its valence shell an
orbital____.
With paired electron (b)
With single electron (c) With no electron (d)With
three electronSolution:
QUESTION NO.
|
ANSWER KEY
|
1.
|
C
|
2.
|
C
|
3.
|
D
|
4.
|
A
|
5.
|
B
|
6.
|
B
|
7.
|
D
|
8.
|
C
|
9.
|
B
|
10.
|
C
|
11.
|
B
|
12.
|
D
|
13.
|
C
|
14.
|
D
|
15.
|
A
|
16.
|
A
|
17.
|
A
|
18.
|
B
|
19.
|
C
|
20.
|
D
|
21.
|
C
|
22.
|
D
|
23.
|
A
|
24.
|
C
|
25.
|
A
|
26.
|
B
|
27.
|
A
|
28.
|
B
|
29.
|
C
|
30.
|
C
|
Get more practice
Q.1 An ionic compound A+ B– is most likely to be formed when

(a) The
ionization energy of A is high and electron affinity of B is low
(b) The
ionization energy of A is low and electron affinity of B is high
(c) Both
the ionization energy and electron affinity of B are high
(d) Both
the ionization energy of A and electron affinity of B are low
Q.2 The number of bonds in nitrogen molecules
(a) one
and one
(b) one and two (c) three sigma only(d) two and one
Q.3 Which of
the following statements is not correct regarding bonding molecular orbitals?
(a) bonding molecular orbitals possess less energy than atomic orbitals from
which they are formed
(b) bonding
molecular orbitals have low electron density between the two nuclei (c) every
electron in the bonding molecular orbitals contributes to the attraction
between atoms
(d) bonding
molecular orbitals are formed when the electron waves undergo constructive
interference.
Q.4 Which of the following molecules has zero dipole moment?
(a) NH3 (b) CHCl3
(c) H2O (d) BF3
Q.5 Which of
the hydrogen halides has the highest percentage of ionic character
(a) HF (b) HBr
(c) HCl (d) HI
Q.6 Which of the following
molecules has unpaired electrons in anti–bonding molecular orbitals
(a) O2 (b) N2
(c) Br2 (d) F2
Q.7 Which of the following involve ionic bonding only?
(a) Li3N (b) NaCl
(c) NCl3 (d) O2
Q.8 Which of the following involve covalent bonding only?
(a) KF (b) KCl
(c) CH4 (d) MgCl2
Q.9 Which of the following molecules has a net dipole
moment?
(a) CO2 (b) CS2
(c) SO2 (d) CCl4
Q.10 H2S has a net dipole moment while BeF2 has zero dipole
moment, because
(a) H2S
molecule is linear while BeF2 is angular
(b) H2S
molecule is angular, while BeF2 molecule is linear
(c) Fluorine
has more electronegativity than S
(d) Be
is more electronegative than S
Q.11 Which of the following ions has larger ionic radius?
(a) Na+ (b) K+
(c) Mg2+ (d) Al3+
Q.12 Which of the following bonds is least polar?
(a) H–Se (b)
P–Cl
(c) H–Cl (d) N–Cl
Q.13 Which one has the least bond angle?
(a) NH3 (b) CH4
Q.14 Coordinate covalent bonds are formed by
(a) sharing
of electrons
(b) donation
of electrons
(c) transference
of electrons
(d) none
of these
Q.15 Which of the following molecules would be expected to
have zero dipole moment?
(a) H2S (b) PF3
(c) TeF6 (d) H2O
Q.16 The bond formed between the
elements of low ionization energy and elements of high electron affinity is
(a) ionic (b) covalent
(c) metallic (d) coordinate
Q.17 The side ways overlap of two–p orbitals to form a bond
is called
(a) sigma bond (b) pi () bond
(c) ionic bond (d) covalent bond
Q.18 The head overlap of p–orbitals of two atoms give rise
to bond called
(a) sigma bond (b) pi () bond
(c) ionic bond (d) covalent bond
Q.19 Which element would be the most electronegative element
with
(a) high
ionization energy (IE) and low electron affinity (EA)
(b) low
ionization energy (IE) and high electron affinity (EA)
(c) low
ionization energy and low electron affinity
(d) high
ionization energy and high electron affinity
Q.20 Which element would be the least electronegative
element with
(a) high I.E. and low E.A. (b) low I.E. and high E.A.
(c) low I.E. and low E.A. (d) high I.E. and low E.A.
Q.21 Which of the following substances has the least ionic
character in its bond?
(a) CCl4 (b) KCl
(c) BeCl2 (d) MgCl2
Q.22 Which of the following best describes ionization
energy?
(a) energy
needed to remove the most loosely bound electron from its ground state
(b) it
decreases from left to right across a period
(c) it
increases down the periodic table
(d) it
is represented by x + e– x– + energy
Q.23 Which one of the following characteristics is not
usually attributed to ionic substances
(a) high melting point (b) deform when struck
(c) crystalline
in solid state
(d) well
defined three dimensional structure
Q.24 Which of the following bond is less polar?
(a) B–Cl (b) C–Cl
(c) H–I (d) C–I
Q.25 Which type of the orbital hybridization and geometry is
used by the central atom of
NH2–?
(a) sp2
hybridization and trigonal planar
(b) sp
hybridization and tetrahedral geometry
(c) sp2
hybridization and trigonal planar
(d) sp3
hybridization and tetrahedral geometry
Q.26 Which of the following
compounds has most likely been formed by covalent bonding of atoms
(a) CaF2 (b) MgO
(c) SiH4 (d) NaCl
Q.27 Identify the compound below which has bonds formed by
an overlap of sp and p–orbitals
(a) BF3 (b) BeCl2
(c) NH3 (d) H2O
Q.28 The most electronegative of these group I element is
(a) Na (b) K
(c) Li (d) Cs
Q.29 The type of bonding in HBr is
(a) ionic (b) polar covalent
(c) non–polar covalent (d) coordinate covalent
Q.30 Which of the following statement is not correct
(a) sigma
bond is weaker than a pi bond
(b) sigma
bond is stronger than a pi bond
(c) double
bond is stronger than a single bond
(d) double
bond is shorter than a single bond
Q.31 Which of the following molecules has a pyramidal
structure?
(a) CH4 (b) NH3
(c) H2O (d) C2H4
Q.32 The bond angle in water is
(a) 109–5o (b) 104.5o
(c) 107.0o
(d) 120o
Q.33 During the formation of chemical bond, the potential
energy of the system
(a) decreases (b) increases
(c) does not change (d) none of these
Q.34 H2O molecule has
(a) no lone pair (b) one lone pair
(c) two lone pairs (d) none of these
Q.35 NH3 molecule has
(a) no lone pair (b) one lone pair
(c) two lone pairs (d) three lone pairs
Q.36 In NH3 the covalent bond formed are due to
(a) s–sp overlap (b) s–sp2 overlap
(c) s–sp3 overlap (d) sp2–sp2 overlap
Q.37 Which of the following is largest atom
(a) Mg (b) Be
(c) Sr (d) Ca
Q.38 As compared to covalent compounds, ionic compounds
generally have
(a) low
melting points and low boiling points
(b) low
melting points and high boiling points
(c) high
melting points and high boiling points
(d) high
melting points and low boiling points
Q.39 The attractive force that holds atoms together in a
molecule is called
(a) force of attraction (b) electrostatic force
(c) bond (d) chemical bond
Q.40 Which of the following bonds will be formed between
alkali metals and halogens
(a) ionic
(b) covalent bond
(c) metallic bond (d) coordinate covalent bond
Q.41 The bond formed between the atoms by mutual sharing of
electrons is
(a) ionic (b) coordinate covalent bond
(c) covalent (d) metallic
Q.42 A chemical bond formed between two similar atoms is
purely
(a) ionic (b) covalent
(c) metallic (d) coordinate
Q.43 On the basis of VSEPR model the geometry of BeCl2 is
(a) linear (b) trigonal
(c) tetrahedral (d) angular
Q.44 On the basis of VSEPR theory,
a molecule with three bond pair and no lone pair of electrons will have a
structure
(a) linear (b) trigonal planar
(c) tetrahedral (d) trigonal pyramidal
Q.45 The geometry of NH3 on the basis of VSEPR model is
(a) trigonal planar (b) trigonal pyramidal
(c) tetrahedral (d) linear
Q.46 In which of the following theories the hybridization is
considered
(a) VSEPR (b) Lewis
(c) molecular orbital (d) valence bond
Q.47 The angle between 3 sp2 hybrid orbital is
(a) 90o (b) 120o
(c) 130o (d) 180o
Q.48 The unhybridized “p” orbital in sp2 hybridization is
(a) parallel
to sp2 (b) in the same plane
(c) perpendicular
to sp2 orbitals
(d) out
of plane
Q.49 Which of the following theories gives the idea of
delocalization of electrons
(a) Lewis theory (b) VSEPR theory
Q.50 The tandency of an atom to attract, a shared electron
pair towards itself is called
(a) electron affinity (b) electronegativity
(c) dipole moment (d) ionization potential
Q.51 Energy needed to remove an electron from its gaseous
atom is called
(a) electron affinity (b) ionization energy
(c) lattice energy (d) electronegativity
Q.52 A bond having partial positive and negative charges is
(a) ionic (b) covalent
(c) polar covalent (d) non–polar covalent
Q.53 A bond formed by the linear overlap of atomic orbitals
is called
(a) sigma (b) ionic
(c) pi (d) polar
Q.54 Which of the following elements is the most
electronegative
(a) Li (b) F
(c) O (d) Cl
Q.55 Some covalent compounds dissolve in water due to
(a) hydrolysis (b) hydration
(c) hydrogen bonding (d) metallic bonding
Q.56 Which of the following compounds will have the lowest
boiling point?
(a) PH3 (b)
ASH3
(c) NH3 (d) SbH3
Q.57 Which of the following molecules has a coordinate bond?
(a) NH4Cl (b) NaCl
(c) HCl (d) AlCl3
Q.58 The half of the difference
between the number of electrons in bonding MO and antibonding MO is called
(a) molecule order (b) bond order
(c) proton order (d) electron order
Q.59 The bond order for He2 molecule is
(a) zero (b)
(c) 1 (d) 2
Q.60 The bond order for H2 is
(a) zero (b)
(c) 1 (d) 1.5
Q.61 The bond order in N2 molecule is
(a) zero (b) 1
(c) 2 (d) 3
Q.62 The bond order in O2 molecule is
(a) 1 (b) 2
(c) 3 (d) zero
Q.63 Which one of the following is diamagnetic
(a) B2 (b) C2
(c) N2 (d) O2–
Q.64 Which one of the following molecule is paramagnetic
(a) B2 (b)
C2
(c) N2 (d) F2
Q.65 Which of the following ions is diamagnetic
(a) O (b) O
(c) O (d) N
Q.66 Pi bond consists of two regions of electron cloud
density
(a) along
the bond axis
(b) along
and perpendicular to bond axis
(c) above
and below the bond axis
(d) none
of these
Q.67 Sigma bond consists of one region of electron density
(a) along
the bond axis
(b) along
and perpendicular to bond axis
(c) above
and below the bond axis
(d) none
of these
Q.68 The electron cloud density is symmetrical along the
bond axis in
(a) sigma bond (b) pi bond
(c) both
sigma and pi bond
(d) neither
sigma nor pi bond
Q.69 The electron cloud density is not symmetrical along the
bond axis in
(a) sigma bond (b) pi bond
(c) both
sigma and pi bond
(d) neither
sigma nor pi bond
Q.70 Covalent bonds are
(a) rigid
and directional
(b) rigid
and non–directional
(c) neither
rigid nor directional
(d) non–rigid
and directional
Q.71 Ionic bonds are
(a) rigid
and directional
(b) rigid
and non–directional
(c) non
rigid non directional
(d) non–rigid
and directional
Q.72 Which of the following statements is correct regarding
the covalent compounds
(a) covalent
compounds do not exhibit isomerism
(b) covalent
compounds exhibit isomerism
(c) covalent
compounds are soluble in water
(d) covalent
compounds are insoluble in non–polar solvents
Q.73 The C–C bond length in ethane (C2H6) is
(a) 154 pm (b) 133 pm
(c) 120 pm (d) 105 pm
Q.74 The C–C bond length in ethene (C2H4) is
(a) 154 pm (b) 133 pm
(c) 120 pm (d) 105 pm
Q.75 The C–C bond length in ethyne is
(a) 154 pm (b) 133 pm
(c) 120 pm (d) 105 pm
Q.76 The atomic radii of the
elements have a general trend of fluctuating periodically throughout the
(a) group (b) period
(c) periodic
table (d) series
Q.77 Which of the following atom has the shortest atomic
radius
(a) N (b) F
(c) O (d) B
Q.78 The half of the single bond length between two atoms in
a molecule is called
(a) ionic
radius of an element
(b) covalent
radius of an element
(c) both
ionic and covalent
(d) none
of these
Q.79 Octet rule is not followed in the formation of
(a) CH4 (b) NF3
(c) BCl3 (d) H2O
Q.80 Select the atom with the largest ionization energy in
the following atoms
(a) N (b) P
(c) AS (d) Sb
Q.81 Select the largest atom in the following atoms
(a) O (b) S
(c) Se (d) Te
Q.82 Which of the following group
of elements on the average has the highest ionization energies
(a) IA (b) IIIA
(c) IVA (d) VIIIA
Q.83 Molecular orbital theory has
(a) the
superiority over the VB theory
(b) the
inferiority over the VB theory
(c) neither
superiority nor inferiority over VB theory
(d) none
of these
Q.84 The bond between H–H is
(a) stronger
than the bond between H–Cl
(b) weaker
than the bond between H–Cl
(c) neither
stronger nor weaker than the bond between H–Cl
(d) none
of these
Q.85 In which of the following molecules, the value of bond
order in maximum
(a) H2 (b) O2
Q.86 When the S–character of hybridized orbital decreases
the bond angle
(a) decreases (b) increases
(c) does not change (d) becomes zero
Q.87 One of the causes of reactions is that the systems
attains the energy state which is of
(a) higher in energy (b) lower in energy
(c) balanced in energy (d) equal in energy
Q.88 The increase in the bond energy of a covalent bond is
due to
(a) electronegativity (b) ionization energy
(c) polarity (d) symmetry
Q.89 The polarity of a molecule is expressed by
(a) bond strength (b) dipole moment
(c) bond length (d) shape
Q.90 Dipole moment of H2O is
(a) 1.85 (b) 1.82
(c) 1.87 (d)
1.83
Comment answers below and don't forget to share and provide suggestions to improve practice MCQs.





No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to comment.Team NUST is here to listen you.